밑바닥부터 시작하는 딥러닝(사이토 고키)라는 책을 읽으면서 딥러닝을 다시 공부해보고 있습니다.
오늘의 배운 것
입력 데이터는 데이터 고유의 특성과 분포를 가지고 있는데, 이를 그대로 사용하게 되면 학습이 느리거나 문제가 발생하는 경우가 많다. 이를 위해 정규화(Normalization)가 필요하다. 정규화를 하면 어떤 feature가 다른 feature를 지배하지 못하도록 한다.
Min-Max 정규화는 최솟값을 0, 최댓값을 1로 잡고 그 사이 값은 0과 1 사이 값으로 변환한다. 하지만 이상치에 많은 영향을 받을 수 있다.
Z-Score 정규화는 평균을 빼고, 표준편차로 나눠서 구하는 정규화이다. 데이터가 표준 정규분포에 해당하도록 바꿔준다.
해본 것
어제부터 Keras 프레임워크의 방식을 흉내내보려고 시도 중이다.
레이어를 추가하는 부분까지 구현해보았다.
def make_sample_data_set_regression2():
x = np.random.randint(999999, size=(300, 2))
y =np.dot(x, np.array([3,-2]) ) + 7
# y = y + (6 * np.random.random_sample((1,y.shape[0])) - 3).flatten()
t = np.reshape(y, (y.shape[0],1))
return x,t
회귀를 테스트 하기 위해 임의로 데이터셋을 만드는 함수이다.
3 * (x_0) - 2 * (x_1) + 7의 값이 정답 값이 되는 것이다.
x_data, t_data = make_sample_data_set_regression2()
net = MultiLayerNet()
net.add_layer(Layer.Dense(1, input_size = 2, activation=Layer.IdentityWithLoss() ))
# net.add_layer(Layer.Dense(5, input_size = 2, activation=Layer.Relu() ))
# net.add_layer(Layer.Dense(1))
x_train, t_train, x_test, t_test = shuffle_split_data(x_data, t_data, 0.2)
레이어를 추가하고, 데이터를 train과 test로 나눈다.
scaler = Scaler.StandardScaler()
x_train = scaler.fit_transform(x_train)
x_test = scaler.transform(x_test)
Z-Score 정규화를 하는 모습이다. x_train에 대해 평균과 표준편차를 구해 x_train을 변환시키고, 이 평균과 표준편차로 x_test도 변환시킨다.
class StandardScaler:
def __init__(self):
self.std_array = None
self.mean_array = None
def fit(self, data):
self.data = data
self.std_array = np.std(data, axis=0)
self.mean_array = np.mean(data, axis = 0)
def transform(self, data):
return (data- self.mean_array) / self.std_array
def fit_transform(self, data):
self.fit(data)
return self.transform(data)
사이킷런 라이브러리에 여러 방식의 스케일링 클래스가 있긴 하지만 쓰고 싶지 않아서 직접 구현해서 흉내내보았다.
result = net.train(
x_train, t_train, x_test, t_test, batch_size = 100, iters_num = 15, print_epoch = 1,
optimizer = Optimizer.SGD()
)
predict_target = np.array([[1200, 500]])
print("target :" ,predict_target, "result : ", net.predict(scaler.transform(predict_target)))
print("done!")
마지막으로 학습시킨다. batch_size(미니 배치 당 개수), iters_num(반복 횟수), print_epoch(몇 번마다 정확도를 출력할 것 인지) 등의 설정을 입력받는다.

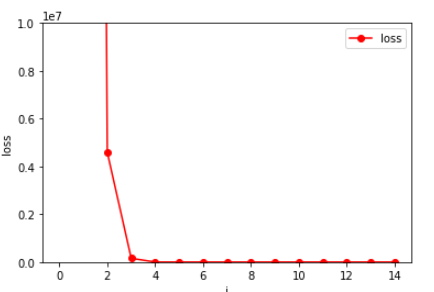
4 epoch 만에 loss가 0에 가까워졌다.
3 * 1200 - 2 * 500 + 7 = 2607 이므로, predict도 잘 이루어진 것을 볼 수 있다.
그런데 왜 여러 층을 더 쌓았을 때 제대로 안 되는 지는 잘 모르겠다. 나중에 케라스로도 돌려보면서 테스트해봐야 할 것 같다.
아직 weight initialization, weight decay 등 갈 길이 멀은 것 같다.
실습한 코드는 https://github.com/woduq1414/deep-learning-without-tensorflow 에 있습니다.
